K2 SmartObjects and K2 Workflows are not limited to only being accessed via K2 SmartForms and Workflows. By using the K2 SmartObject & Workflow API’s you can access SmartObjects and their methods as well as create and start workflows through code.
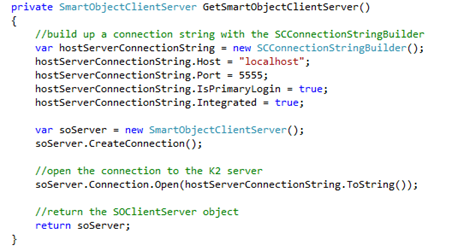
To access K2 SmartObjects you need to connect to the SmartObject Client Server
K2 Automated Testing Software
BenchQA allows full test automation of K2, including fully automated K2 SmartForms and K2 Workflow testing. It promotes test driven development for K2 and ensures continued quality assurance for K2 solutions. Easily apply changes to test cases to accommodate changes to K2 apps and ensure all apps are regression tested to avoid defects and assure continuous quality.
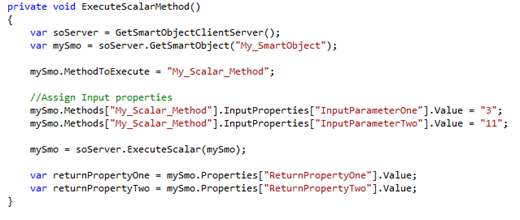
Once you have established your connection to the SmartObject Client Server you need to “Get” the SmartObject, specify the input properties and finally execute the SmartObject.
Methods can be in the form of either scalar or list (to name a few) which you can define when executing the SmartObject.
It is important to note that the SmartObject and Method names are the names stored by K2 which is usually not identical to the names you created them with. For example, if you create a SmartObject called “My.SmartObject”, K2 will likely save it as “My_SmartObject”. The same applies to method names.
The K2 SmartObject tester can be used to inspect the exact names K2 assigned to SmartObjects and Methods. An easy way to inspect is to generate a C# class for the SmartObject – this opens a C# class will all methods, properties and the SmartObject defined as it is saved by K2.
Another important note is that input parameters that are mapped to ServiceObject method parameters will result in an error when you try to assign them via code. For properties to resolve correctly they need to be mapped directly to a SmartObject property.
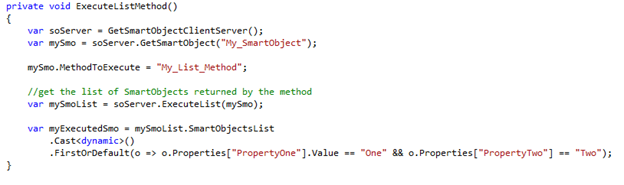
When executing a list method gaining access to the results are usually shown as looping through the list. Depending on what you need to do with the results this can be improved by casting the SmartObjecsList as a dynamic object and then using LINQ.
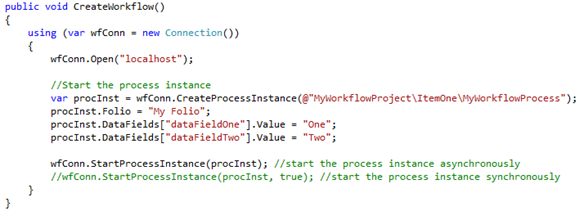
To create and start a K2 Workflow the approach is similar. You create a workflow connection and specify the process instance, folio as well as data fields (if necessary). A process instance with the project layout shown in the snippet above will have a process name as shown in the code snippet below.
The workflow can be started either synchronously or asynchronously as shown in the code snippet above.